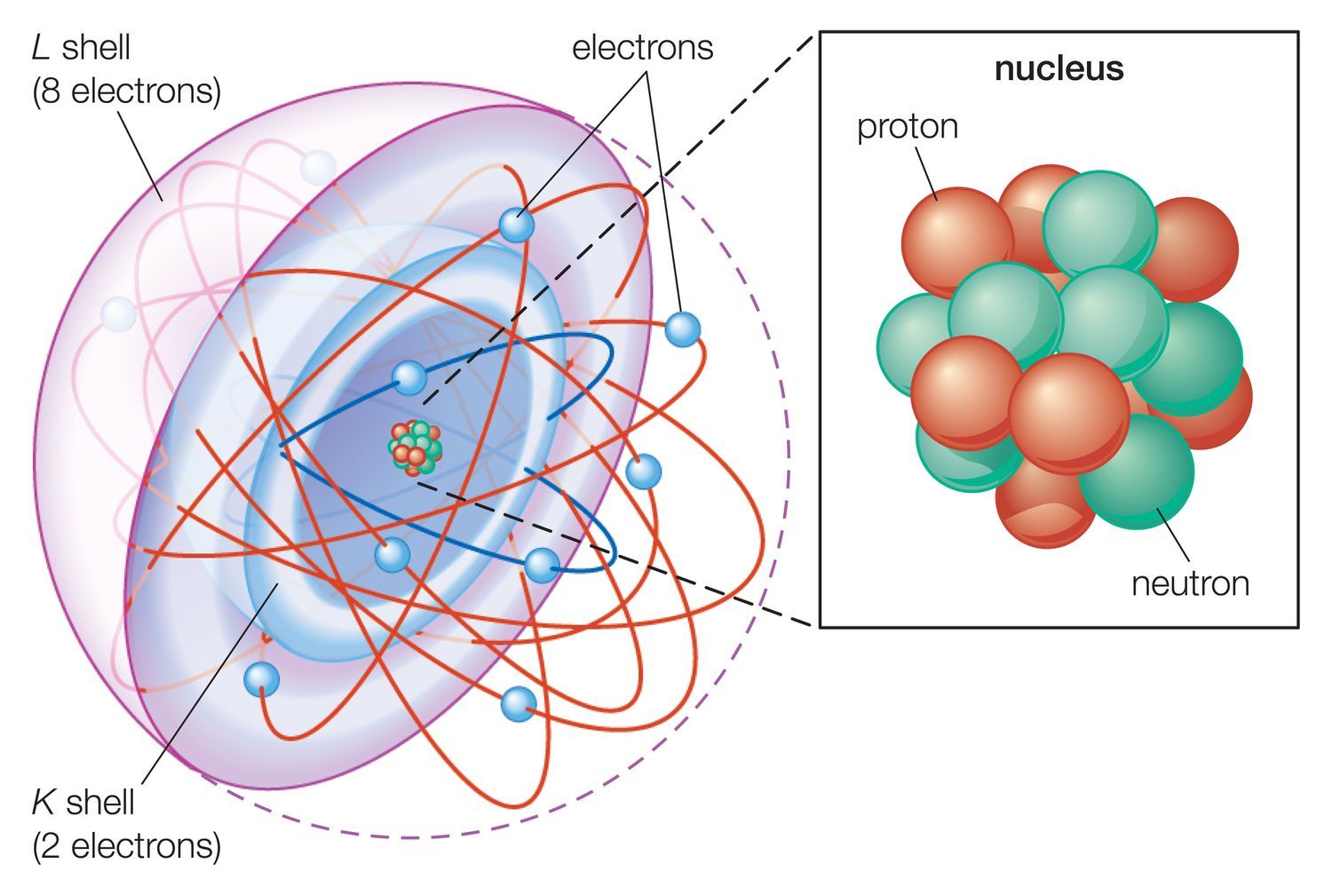
This is an alphabetical electron configuration list of all the elements of the periodic table. While the electronic structure of the lighter elements is well-studied, once you get to the heavier man-made elements, these configurations are predicted or calculated based on periodic table trends. Configurations are estimated from dubnium (element 105) up to ununoctium (element 118).
Noble Gas Core Notation Used
Note the configurations are listed using the noble gas core notation. So, for example, neon is written using this shorthand as [He]2s22p6 rather than 1s22s22p6. The electron configurations of the newly discovered super-heavy elements are predicted. Electrons travel at relativistic speeds in these atoms, so unusual behavior might occur.
Lectura relacionada: Por qué la Entalpía Estándar de Formación de O2 Es Igual a Cero
Por qué la Entalpía Estándar de Formación de O2 Es Igual a CeroYou may also view the electron configurations of the first 104 elements in order of atomic number.
Actinium to Curium
Actinium - [Rn]6d17s2
Aluminum - [Ne]3s23p1
Americium - [Rn]5f77s2
Antimony - [Kr]4d105s25p3
Argon - [Ne]3s23p6
Arsenic - [Ar]3d104s24p3
Astatine - [Xe]4f145d106s26p5
Barium - [Xe]6s2
Berkelium - [Rn]5f97s2
Beryllium - [He]2s2
Bismuth - [Xe]4f145d106s26p3
Bohrium - [Rn]5f146d57s2
Boron - [He]2s22p1
Bromine - [Ar]3d104s24p5
Cadmium - [Kr]4d105s2
Calcium - [Ar]4s2
Californium - [Rn]5f107s2
Carbon - [He]2s22p2
Cerium - [Xe]4f15d16s2
Cesium - [Xe]6s1
Chlorine - [Ne]3s23p5
Chromium - [Ar]3d54s1
Cobalt - [Ar]3d74s2
Copernicium (formerly ununbium) - [Rn]5f146d107s2
Copper - [Ar]3d104s1
Curium - [Rn]5f76d17s2
Darmstadtium to Hydrogen
Darmstadtium - [Rn]5f146d97s1
Dubnium - [Rn]5f146d37s2
Dysprosium - [Xe]4f106s2
Einsteinium - [Rn]5f117s2
Erbium - [Xe]4f126s2
Europium - [Xe]4f76s2
Fermium - [Rn]5f127s2
Flerovium (formerly ununquadium) - [Rn]5f146d107s27p2
Fluorine - [He]2s22p5
Francium - [Rn]7s1
Gadolinium - [Xe]4f75d16s2
Gallium - [Ar]3d104s24p1
Germanium - [Ar]3d104s24p2
Gold - [Xe]4f145d106s1
Hafnium - [Xe]4f145d26s2
Hassium - [Rn]5f146d67s2
Helium - 1s2
Holmium - [Xe]4f116s2
Hydrogen - 1s1
 Si una Molécula Se Oxida, ¿Gana o Pierde Energía?
Si una Molécula Se Oxida, ¿Gana o Pierde Energía?Indium to Moscovium
Indium - [Kr]4d105s25p1
Iodine - [Kr]4d105s25p5
Iridium - [Xe]4f145d76s2
Iron - [Ar]3d64s2
Krypton - [Ar]3d104s24p6
Lanthanum - [Xe]5d16s2
Lawrencium - [Rn]5f147s27p1
Lead - [Xe]4f145d106s26p2
Lithium - [He]2s1
Livermorium (formerly ununhexium) - [Rn]5f146d107s27p4
Lutetium - [Xe]4f145d16s2
Magnesium - [Ne]3s2
Manganese - [Ar]3d54s2
Meitnerium - [Rn]5f146d77s2
Mendelevium - [Rn]5f137s2
Mercury - [Xe]4f145d106s2
Molybdenum - [Kr]4d55s1
Moscovium - [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p3 (predicted)
Neodymium to Protactinium
Neodymium - [Xe]4f46s2
Neon - [He]2s22p6
Neptunium - [Rn]5f46d17s2
Nickel - [Ar]3d84s2
Nihonium - [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p1 (predicted)
Niobium - [Kr]4d45s1
Nitrogen - [He]2s22p3
Nobelium - [Rn]5f147s2s2
Oganesson - [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p6 (predicted)
Osmium - [Xe]4f145d66s2
Oxygen - [He]2s22p4
Palladium - [Kr]4d10
Phosphorus - [Ne]3s23p3
Platinum - [Xe]4f145d96s1
Plutonium - [Rn]5f67s2
Polonium - [Xe]4f145d106s26p4
Potassium - [Ar]4s1
Praseodymium - [Xe]4f36s2
Promethium - [Xe]4f56s2
Protactinium - [Rn]5f26d17s2
Radium to Tungsten
Radium - [Rn]7s2
Radon - [Xe]4f145d106s26p6
Rhenium - [Xe]4f145d56s2
Rhodium - [Kr]4d85s1
Roentgenium - [Rn]5f146d107s1
Rubidium - [Kr]5s1
Ruthenium - [Kr]4d75s1
Rutherfordium - [Rn]5f146d27s2
Samarium - [Xe]4f66s2
Scandium - [Ar]3d14s2
Seaborgium - [Rn]5f146d47s2
Selenium - [Ar]3d104s24p4
Silicon - [Ne]3s23p2
Silver - [Kr]4d105s1
Sodium - [Ne]3s1
Strontium - [Kr]5s2
Sulfur - [Ne]3s23p4
Tantalum - [Xe]4f145d36s2
Technetium - [Kr]4d55s2
Tellurium - [Kr]4d105s25p4
Tennessine - [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p5 (predicted)
Terbium - [Xe]4f96s2
Thallium - [Xe]4f145d106s26p1
Thorium - [Rn]6d27s2
Thulium - [Xe]4f136s2
Tin - [Kr]4d105s25p2
Titanium - [Ar]3d24s2
Tungsten - [Xe]4f145d46s2s2
 Si Una Molécula Se Reduce, ¿Gana o Pierde Energía?
Si Una Molécula Se Reduce, ¿Gana o Pierde Energía?Ununoctium to Zirconium
Ununoctium - [Rn]5f146d107s27p6
Ununpentium - [Rn]5f146d107s27p3
Ununseptium - [Rn]5f146d107s27p5
Ununtrium - [Rn]5f146d107s27p1
Uranium - [Rn]5f36d17s2
Vanadium - [Ar]3d34s2
Xenon - [Kr]4d105s25p6
Ytterbium - [Xe]4f146s2
Yttrium - [Kr]4d15s2
Zinc - [Ar]3d104s2
Zirconium - [Kr]4d25s2
Reference: Element data from Wolfram Alpha, retrieved 06/09/2015